What does everyone do in UI/UX, but in different ways? The answer is the design process. Enacting the correct design project process is essential for creating any product. Actually, whether it is UI/UX or graphic design creative process, it all goes through almost similar steps. But today, we will talk specifically about user experience design.
Designing a product is a difficult journey. It is where the needs of the user come to the fore. If the design team sticks to this strategy, they can create a great product that will be in high demand. In this article, we will define what is the design process, which steps it takes, and how to improve it.
But first, we will talk about the UI/UX design itself. It is the backbone of the whole process. If you understand the meaning of UI / UX in general, then many of the steps will become more evident. It is needed for a better understanding of what is the design process. Ready?
What is UI/UX design?
So, what does UI/UX mean? To understand the whole picture clearly, we need to start from the basics. To tell a long story short, let’s keep in mind that UX stands for the term “user experience design.” So, in essence, UX may apply to anything that can give the experience, whether it is a website or app or a visit to the supermarket or brand image.
The “user experience” part of the term is about interactions between users and a product or service. It is not affiliated with visuals. UX is about the overall feel of the product use. To achieve the best results, UX designers care about the simplicity for the users in reaching their goals when using a product or service.
At Axicube, we believe that good UX cares about the user and solves business problems. And the task of the designer is to achieve precisely this: to help the company achieve success so that a person is comfortable in the process of using the final product.
The UI design stands for “user interface.” The user interface design process focuses on aesthetics and style. The goal of UI designers is to make an interface that is good-looking and pleasurable to use. In short, UI designers aim to create the perfect design so that the final product will be enjoyable, frustrating-free, and communicate brand values. Yet, 52% of users say the main reason why they won’t return to a website is aesthetics. It makes you wonder, doesn’t it?
Why does UI/UX matter?
It may sound too dramatic, but online businesses are now fighting a digital war. Everyone tries to increase their visibility on the Internet. UI/UX directly relates to the achievement of this goal. Nowadays, it is not enough just to have some kind of website that works under the name and logo of your company. According to statistics, 88% of users are less likely to return to a website after a bad user experience.
You have to invest more in your website to make it stand out from the thousands. Every $1 invested in UX results in a return of $100 (ROI = 9,900%). First, the most attention should be paid to your site’s user experience and interface because it’s all about your users. Therefore, you need to make your site or application pleasant to use and good-looking. Things that would explain why do UI/UX matters for your business:
-
Usability
It makes sense that users will only visit websites and applications that are convenient and easy to use. Therefore, you need to ensure that your product can be used without confusion. It is where a great UI / UX collaboration comes in handy. A quality experience can do wonders for your business. Even the statistics claim that 70% of online businesses fail because of bad usability.
-
Business growth
The success of a business directly depends on the satisfaction and comfort of the user. The more you satisfy the user, and the more comfortable your product is to use, the more customers you will have, and the more your business will grow accordingly. Therefore, investment in UI / UX is necessary. In addition, it is essential to make sure that your website and application are user-friendly.
-
Engagement
The excellent UI/UX makes things visually appealing and engaging. People need only a few seconds to understand if they like the visuals of your app or website. That’s why it is vital to invest in your product’s good UI/UX design.
To finally convince you that UI/UX is important for your business, here are some data from Forrester’s research: a well-designed UI could raise your website’s conversion rate by up to 200%, and a better UX design could yield conversion rates up to 400%. That is impressive, right? Now that we’ve covered what UI/UX is and why it’s so crucial to business, let’s find out how the magic happens. More precisely, what is the design process, and what stages of product design are in it.
What is the design process?
A design process describes a designers’ journey to solving any problem. How does it look? Well, it depends on the product you are designing. But something remains the same. The design process definition claims it is an approach for splitting a large project into manageable parts.
The famous designer and cognitive psychologist Donald Norman said: “I invented the term because I thought human interface and usability were too narrow. I wanted to cover all aspects of the person’s experience with the system including industrial design, graphics, the interface, the physical interaction, and the manual.”
Designing a product includes the process of finding the answers to questions like “Why?”, “What?” and “How?”. The “Why?” is about finding users’ motivation or reason for using the product. The “What?” goes to the actions users need to perform while using it. And “How?” is about creating better functionality and look.
Well, it is good to have a great guide about a well-tried UX design process that you can rely on. In this article, we will show you the steps of the design process. It can be used in any field, but we use it while working on our projects. If you want to see the design process example, read our previous article about creating an employee onboarding app. There we described our work on a specific project. It is a great product design process example.

How to Improve Employee Onboarding with Yangol.io | Case Study
What are the Steps of the Design Process?
Starting a new project can be tricky. To avoid procrastination and unnecessary actions, you need to have stable stages of design process. And this is the answer to the question, “why do we use a design process?”. If the design team has a clear plan of action, their efforts are not wasted on unnecessary activities, and everyone knows what needs to be done next.
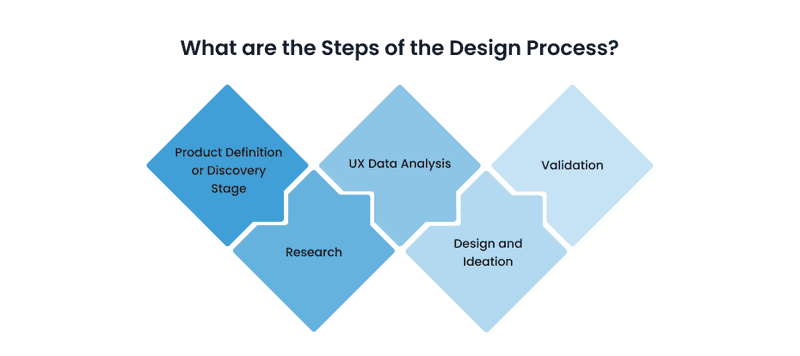
At Axicube, we have stable product design process steps, so we decided to share them with you in this article. The design project process can be divided into five stages. After each phase, an iteration is carried out, allowing identifying errors in the early stages. Also, these steps will help bring the design to perfection. So, if the question “why do we use a design process?” arises in your head, here is the answer: it makes our work more productive.
The proper process gives you a clear understanding of how to design a new product. So, let’s dive into this!
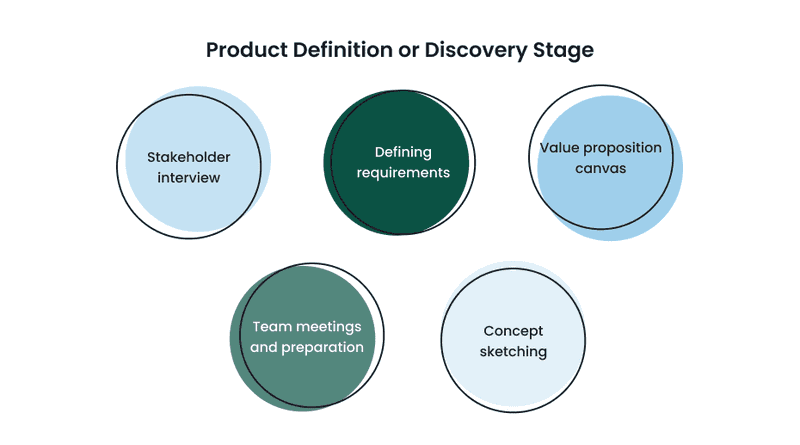
Product Definition or Discovery Stage
So you are asking, “what is the first step of the design process?”. It is all about product definition and finding some skeletons. Before diving into design processes, it is crucial to understand its context for existence. It is the basis for a future project. The design team needs to understand all the pitfalls and assign work responsibilities. This design process activities include:
-
Stakeholder interview
First, a stakeholder interview is conducted to understand their business’s core values and goals. Also, in this interview, the main expectations from the final result are indicated.
-
Defining business, user, and technical requirements
In general, the business requirements that designers need to identify cover the main goals that the company or startup that the client represents wants to achieve. These requirements are usually collected during the stakeholder interviews we discussed above. User requirements are basically about users’ pain points and goals that may be achieved using the future product. Finally, the technical specifications cover the features that should be included and the product’s usability and maintenance.
-
Value proposition canvas
It is a diagram that describes how your product is beneficial and what problems it will solve for your customer. It is helpful not only from a marketing point of view but also from a functional planning point of view. The stakeholder often participates in this product design phase since they know best what their consumers need.
-
Team meetings and preparation
A detailed work plan is drawn up during this meeting, and possible challenges are determined.
-
Concept sketching
After the stakeholder expectations and business goals are outlined, the future product is sketched. These can be sketches on paper or very low-fidelity concepts.
Usually, this design process stage ends with a kick-off meeting. It is essential to set proper expectations for both sides, define team structure, communication channels, and set KPIs (Key Performance Indicator) so it will be possible to measure the success of the final product.
Yet, the design brief comes up at the end of this step. It is the document that describes the vision and concept of the future project, its goals, KPIs, and planned scope of work. The following product design stage is research. So, let’s take a closer look.
Research
Once stakeholder defines the idea, the design team starts the research phase. It includes market and user persona research. If it is done right, it will save time in the future, both for the business and design team. In addition, good research will help designers to make good decisions.
Why? Because the better they understand users’ needs, the better design solutions they will make. Remember that if the design ignores people, then people ignore the design. So what is the point of ignoring the user and market research phase? Let’s instead move from reasoning to design process activities in this phase:
-
Competitive research
It helps designers to understand the industry and thus make more suitable solutions.
-
Domain analysis
It is another type of immersion in the industry business environment. The design team analyzes how users of a specific niche behave to understand the product’s essential functionality.
-
User interview and audience survey
A good product experience starts with a good understanding of the users. Individual user interviews provide quality data about the target audience, such as their needs, wants, motivations and behavior.
-
Service Blueprint map
It is a diagram that visualizes the interactions between the various components - people, devices, and processes - directly related to touchpoints in a particular customer journey.
-
Analysis and audit of the current product
Suppose there is already a finished product or part of it. In that case, the design team conducts an audit to identify weaknesses and improve everything or even add something new to improve the product.
Read our previous article if you have a ready-made product and are interested in learning more about its audit. In it, we analyze this process in detail. But in this article, we will go further.

How to boost performance with UX audit (and who can do this for you)
So, what is about research? This product design phase is quite variable. Everything depends on the complexity of the project, available sources, and other factors. At the end of this stage, the interaction comes, and previous steps repeat if something is not as good as expected.
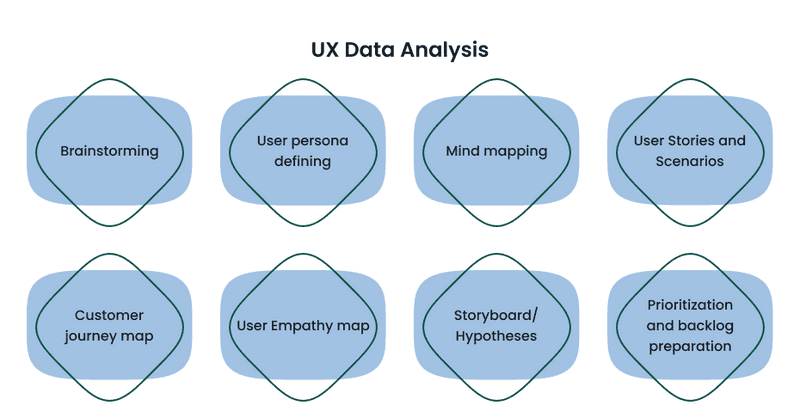
UX Data Analysis
During this product design stage, the design team analyses data gathered before. Then, after defining user personas, designers start thinking about attracting users and how they will act using the future product. At this stage, many ideas come up, and the product’s vision becomes more evident. So how the analysis goes?
-
Brainstorming
The product owner is also involved in this process. Many different ideas are collected during brainstorming. Finally, the most suitable for the needs of the business and its consumers are selected.
-
User persona defining
This part of the design process is vital for understanding the stakeholder’s business’s audience. Suppose they already have all the information about this. In that case, the designers carry out another little research to determine the user personas with even more accuracy. That is to create the perfect UX.
-
Mind mapping
It is a visualization tool that helps structure information and understands the relationships between elements. Elements can be keywords, ideas, concepts. With this tool, the design team can develop new ideas and see the logic and train of thought.
-
User Stories and Scenarios
Designers create it to show how users would achieve their goals using the product. User scenarios help to create great UX and improve usability.
-
Customer journey map
It is the visual representation of the customer journey with all touchpoints. It helps to understand the crucial parts of the project.
-
User Empathy map
It is a method that allows you to put yourself in the user’s shoes, to look at the problem that your product solves through their eyes. It can be used both as an alternative to user personas and as an addition to them. An empathy map is a diagram in the center of which a representative of a specific user segment is placed; on opposite sides of it, there are four blocks (“think and feel,” “say and do,” “see,” “hear”). Finally, the findings are presented in two additional blocks: “problems and pain points” and “values and achievements.”
-
Storyboard/Hypotheses
It is a tool that helps the design team visually predict and study the user’s experience of using the product. It helps to understand how people will interact with the product over time and gives a clear idea of creating a human-centered design.
-
Prioritization and backlog preparation
Ideally, a product backlog should list all the product-related tasks that the design team needs to accomplish and everything they can and focus on (over some time) after that.
It’s crucial to prioritize the backlog of work to avoid an open list of all random thoughts about your product. Instead, the backlog should be structured, organized, and ordered to prioritize the most strategically important things the team can work on.
After all these design process activities are done, it is time to start designing. At the end of this stage, designers clearly understand what needs to be included in the product and how to make it attractive to the users. If the enlightenment did not happen, previous steps need to be repeated until it happens.
Design and Ideation
When the needs, desires, expectations of users are established and how they will behave to achieve their goals using the product, it is time for magic. The creative design process looks magical, right?
Well, if you want to dive into the magic of visual design, read our previous article about it. There, we talk about the difference between visual and UI design and why is it important to make your product attractive.

Take My Money: Visual Design vs UI Design as a Method to Make Selling Product
But let’s return to the topic. First, designers do wireframes to determine the approximate structure of a future application or website, followed by low-fidelity prototypes and high-fidelity ones. There are many iterations with the stakeholder at this stage of the design process. But why can’t you do it for the perfect design?
Let’s take a closer look at design process activities in this phase:
-
Information architecture/Flowchart
It is all about how the content will be structured and presented to the users who interact with the product.
-
Rapid prototyping
It is about quickly laying out UI screens or user flows and adding interactivity so that designers, potential users, and a side product owner can test the concept. UI design dictates how something should look, whereas Rapid Prototyping dictates how it should feel and behave. Done right, it will allow you to be sure of exactly how the product will look and feel, and it will save a lot of time in the product development process.
-
Wireframing
Wireframing is the process of creating a skeletal outline of future design. This UX design process involves sketching interactive products to determine the structure and sequence of possible design decisions. These schemes reflect the needs of users and businesses. These mockups help teams and product owners create optimal, user-centric prototypes and products.
If you would like to know more about the wireframing process, read our article about that!

What is a Wireframe and Why Do You Need it in the Design Process
-
User flows
It is a diagram that shows how the user takes through your product from the beginning and the final touchpoint.
-
High-fidelity prototypes
A high-fidelity prototype is a close view of how the product will look at the final. It may contain moving graphics or elements that the user can manipulate. It is excellent for testing on real users.
-
Design system
If the project is large, designers create a system of components and patterns, making it easier to pass it to the developers.
Read our previous article if you’d like to learn more about this step in the design process. In it, we analyze how visual affects the performance of your business, what principles should be followed, how to attract an audience using the proper UI, and much more.

UI/UX Concept for Your Product: Where Art and Usability Meet
Let’s get back to the main topic, though. The prototypes are great for testing it in real users to gather feedback. It is vital to consider all the wishes and edits from users to make the user-centered design. So it is time to test ideas!
Validation
Usually, this product design stage starts after creating high-fidelity prototypes because they are perfect for testing on real users. Then, in a series of user testing, the team tests the product hypotheses on both stakeholders and users.
-
A/B testing
This method is perfect if there are few ideas and it is challenging to choose which one is better. Let users decide. Users are divided into two groups, each given a different design version. It allows designers to see how each version works and get users’ most positive feedbacks. Thus, it is possible to test alternative design implementations (landing page, design features, etc.) and choose the right one.
-
In-house testing
It is when team members try to use the product as users. Then, they complete regular operations to detect any flaws.
-
Surveys
It is an excellent tool for collecting information from real users. For example, UX designers can add open-ended questions such as, “What would you change about the product to make it better?” to determine what users think about specific features.
-
Analytics
Analytics tools allow gathering data about clicks, navigation time, and other activities to understand how users interact with the product. It is an essential part of the design process.
Now, you have learned about the whole product design cycle. You might ask why it is a “cycle,” and the answer is - it is so because each phase can be repeated after iteration. For example, if something goes wrong, the team repeats previous product design steps until everything becomes perfect.
With the knowledge of the step by step design process, we can go to the tips that would improve it.
How to Improve Creative Design Process: Tips to Follow
Nothing is perfect. Also, even if you know the step-by-step design process, there is still room for improvement. But how? Let’s take a look at some tips:
-
Improve design to developer handoffs
To make it, organize the information and all files correctly. The developer shouldn’t be confused with strange file names or else. Yet, include developers in the design process to be on the same page.
-
Test early designs
To create a user-centered design, test your ideas as many times as possible. It will give you invaluable feedback with which it is possible to make the perfect product.
-
Don’t be afraid to experiment
Sometimes ideas seem ridiculous at first glance, but then it turns out into a great design solution. So don’t be afraid to experiment. Give yourself freedom for action. Yet, every voice should be heard. So don’t ignore any ideas because they can be the answer.
-
Design is never done
To iterate, you must first create. Next, show your work to a stakeholder or other design team. Then ask them how to make the idea better (instead of relying solely on your instinct). The quickest way to achieve perfection is to admit that you need feedback. Also, there is always something to complete or improve in design. Try to get more feedback to understand what else can be improved.
-
Team meeting hygiene
The meeting should only ad value to the participants. Delete all useless meetings from the calendar. Every participant should get ready for the session to discuss only essential things. Yet, it is crucial to be able to listen.
-
Focus on communication
Make sure that everyone is on the same page. The design team needs to provide regular design review sessions to do this. It would also be helpful because the design team will get iterations from stakeholders with each session.
It is the bulk of what can be improved in the design process. If you want to learn more about how to assign responsibilities in the process when you need to work with the design and development team, read our previous article. We analyze all aspects of collaboration between designers, developers, and product owners in detail.
A Love Story Between Developers, Designers, and PO. How to Organize the Design Process to Archive a Happy Ending?
Conclusion
There is no “one size fits all” roadmap for the UI/UX design process. But no matter which method you follow, the goal of each design process is the same: to create an excellent product for your users. So use what works best for your project, get rid of everything else, and evolve your design process as far as you feel comfortable.
However, the product design process always starts with the business goals definition and understanding the target audience. With that, it is possible to create a memorable user experience. Yet, understanding the whole product design cycle is helpful not only for the designers. It would also help the stakeholder to understand inner processes.
We have shown you the example of the design process that we use at Axicube. Our team has excellent experience working with different startups and businesses from various market segments. We have developed a stable product design process for ourselves throughout our work, which helps us cope with tasks of varying complexity. If you want to bring your idea to life and participate in our design process as a stakeholder, we are open to cooperation.